Web-based technology has dramatically improved our ability to detect communicable disease outbreaks, with the potential to reduce morbidity and mortality because of swift public health action.
Apps accessible through the internet and on mobile devices create an opportunity to enhance our traditional indicator-based surveillance systems, which have high specificity but issues with timeliness.
Objective: The aim of this study is to describe the literature on web-based apps for indicator-based surveillance and response to acute communicable disease outbreaks in the community with regard to their design, implementation, and evaluation.
Results: Apps were primarily designed to improve the early detection of disease outbreaks, targeted government settings, and comprised either complex algorithmic or statistical outbreak detection mechanisms or both.
We identified a need for these apps to have more features to support secure information exchange and outbreak response actions, with a focus on outbreak verification processes and staff and resources to support app operations.
Conclusions: Public health officials designing new or improving existing disease outbreak web-based apps should ensure that outbreak detection is automatic and signals are verified by users, the app is easy to use, and staff and resources are available to support the operations of the app and conduct rigorous and holistic evaluations.
read the study at https://publichealth.jmir.org/2021/4/e24330
Lire l'article complet sur : publichealth.jmir.org
Via nrip



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

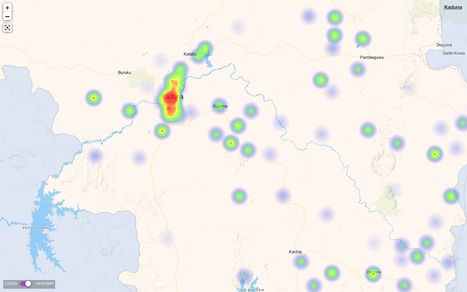







The large scale adoption and constant improvement of these kind of tools - i.e. Tools for Identifying, managing and responding to Infectious Disease Outbreaks in Communities should have started 10 years ago. This is one of my favorite areas of #DigitalHealth. Having been the architect of a number of successful Epidemic Detection and Prediction systems, I feel in this area of Digital Health we still have a long way to go till we reach level where Epidemic Management Teams trust the systems more than their Ears on the ground.
But I know that with constant effort, regular additions of modern data paradigms , regular effort and improvement and interdisciplinary cooperation, a point in time where outbreaks can be contained before they occur will come by. Thought that day is out there in the future ,that its possibility alone should drive us forward.
To learn about or have a demo of Plus91's Early Warning and Outbreak Detection System which is based on the principles of Syndromic Surveillance and Machine Learning, please contact me via the form with the words "Surveillance Demo" in the message. I promise you it is unlike what you would have seen elsewhere.