Adherence to treatment is critical for successful treatment outcomes.
Although factors influencing antiretroviral therapy (ART) adherence vary, young adults are less likely to adhere owing to psychosocial issues such as stigma, ART-related side effects, and a lack of access to treatment.
The Call for Life Uganda (CFLU) mobile health (mHealth) tool is a mobile phone–based technology that provides text messages or interactive voice response functionalities through a web interface and offers 4 modules of support.
Objective: This study aims to describe the acceptability and feasibility of a mobile phone support tool to promote adherence to ART among young adults in a randomized controlled trial.
Methods: An exploratory qualitative design with a phenomenological approach at 2 study sites was used. A total of 17 purposively selected young adults with HIV infection who had used the mHealth tool CFLU from 2 clinics were included. In total, 11 in-depth interviews and 1 focus group discussion were conducted to examine the following topics: experience with the CFLU tool (benefits and challenges), components of the tool, the efficiency of the system (level of comfort, ease, or difficulty in using the system), how CFLU resolved adherence challenges, and suggestions to improve CFLU. Participants belonged to 4 categories of interest: young adults on ART for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission, young adults switching to or on the second-line ART, positive partners in an HIV-discordant relationship, and young adults initiating the first-line ART. All young adults had 12 months of daily experience using the tool. Data were analyzed using NVivo version 11 software (QSR International Limited) based on a thematic approach.
Results: The CFLU mHealth tool was perceived as an acceptable intervention;
young adults reported improvement in medication adherence, strengthened clinician-patient relationships, and increased health knowledge from health tips.
Appointment reminders and symptom reporting were singled out as beneficial and helped to address the problems of forgetfulness and stigma-related issues.
HIV-related stigma was reported by a few young people. Participants requested extra support for scaling up CFLU to make it more youth friendly.
Improving the tool to reduce technical issues, including network outages and a period of software failure, was suggested. They suggested that in addition to digital solutions, other support, including the promotion of peer support meetings and the establishment of a designated space and staff members for youth, was also important.
Conclusions: This mHealth tool was an acceptable and feasible strategy for improving ART adherence and retention among young adults in resource-limited settings.
read the entire study at https://mhealth.jmir.org/2021/6/e17418/
Via
nrip



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
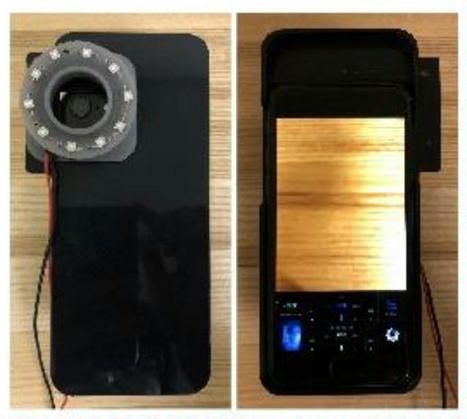















The use of mobile tools for data capture and AI/ML algorithms for diagnostics and detections has been the inside story of digital health over the past 4 years. This is an excellent study and shows the promise of this combination of technologies in building the future of healthcare. HIV is a pandemic which must be eradicated.